헨리 민츠버그(Henry Mintzberg)는 조직 이론 분야에서 중요한 연구를 한 학자로, 조직을 그 구조와 기능에 따라 여러 유형으로 분류했습니다. 민츠버그는 조직을 6가지 유형으로 구분했으며, 각 조직 유형은 조직의 크기, 환경, 목표, 관리 방식 등에 따라 다르게 나타납니다. 민츠버그의 조직 유형 이론은 조직의 구조가 어떻게 이루어지고, 각 구조가 어떻게 운영되는지에 대한 통찰을 제공합니다.
민츠버그는 조직을 "조직의 구성 요소"와 "조직의 환경"을 고려하여 6가지 주요 구조로 분류했습니다. 각 유형은 특정한 특징과 장단점을 가지고 있으며, 조직의 목적과 운영 방식을 이해하는 데 중요한 역할을 합니다.
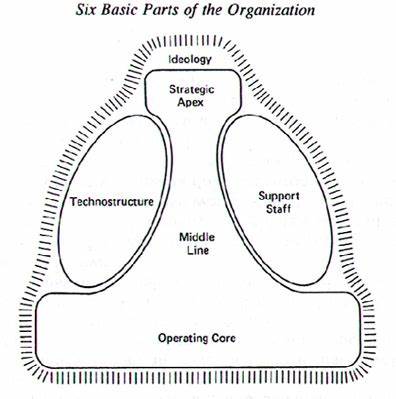
민츠버그의 조직유형
1. 기계적 조직 (Machine Bureaucracy)
- 특징: 기계적 조직은 엄격한 규정과 정해진 절차에 의해 운영되는 조직입니다. 모든 업무가 표준화되어 있으며, 명확한 역할 분담과 중앙집중적인 의사결정 구조가 특징입니다. 대기업이나 정부 기관에서 흔히 볼 수 있는 구조입니다.
- 구성요소:
- 운영층 (Operating Core): 일상적인 업무를 수행하는 직원들.
- 중간관리층 (Middle Line): 상위 관리자와 운영층을 연결하는 중간 관리자의 역할.
- 지원 기구 (Support Staff): 경영진과 일선 직원들을 지원하는 부서들.
- 전문직 관리층 (Technostructure): 업무의 표준화, 규격화, 절차 수립 등을 담당하는 전문가들.
- 최고경영층 (Strategic Apex): 조직의 전략을 수립하고, 의사결정을 내리는 경영진.
- 장점: 효율적이고 예측 가능한 운영, 대규모 조직에 적합.
- 단점: 창의성과 유연성이 부족하고, 환경 변화에 대응하기 어려울 수 있습니다.
2. 전문적 조직 (Professional Bureaucracy)
- 특징: 전문적 조직은 높은 수준의 전문성을 요구하는 조직으로, 전문직 종사자들이 자율적으로 업무를 수행하는 구조입니다. 병원, 대학, 회계법인 등에서 많이 볼 수 있습니다. 각 전문가는 일정한 규칙과 절차를 따르지만, 독립적으로 업무를 처리합니다.
- 구성요소:
- 운영층 (Operating Core): 각 전문직 종사자들이 자율적으로 업무를 수행합니다.
- 중간관리층 (Middle Line): 전문직 종사자들이 자율적으로 업무를 처리하도록 관리하고 조정합니다.
- 최고경영층 (Strategic Apex): 조직의 전략적 목표를 수립하고, 상위 관리자는 전문직 종사자들이 자율적으로 업무를 할 수 있도록 지원합니다.
- 장점: 전문성에 따른 높은 수준의 서비스 제공, 높은 자율성.
- 단점: 각자의 전문성에 따른 독립성이 강해 협력이 부족할 수 있고, 통제가 어려운 경우가 있습니다.
3. 사업부제 조직 (Divisionalized Form)
- 특징: 사업부제 조직은 조직을 여러 개의 독립적인 사업 부문으로 나누어 운영하는 형태입니다. 각 부문은 독립적인 관리 체계를 갖추고 있으며, 중앙에서는 전체 전략과 자원 배분을 관리합니다. 대기업에서 다양한 제품군이나 지역별로 독립적인 부서를 운영할 때 사용됩니다.
- 구성요소:
- 사업부 (Divisions): 각 사업 부문은 독립적으로 운영되며, 자체적인 관리와 자원 관리를 담당합니다.
- 전문직 관리층 (Technostructure): 각 부문의 업무를 표준화하고, 지원하는 역할을 합니다.
- 최고경영층 (Strategic Apex): 전체적인 전략을 수립하고, 자원 배분을 담당합니다.
- 장점: 각 사업 부문이 독립적으로 운영되어 빠르게 변화하는 시장에 적응할 수 있습니다.
- 단점: 각 사업 부문 간의 자원 중복이나 협력 부족, 전체 조직의 일관성이 떨어질 수 있습니다.
4. 애드호크러시 (Adhocracy)
- 특징: 애드호크러시는 매우 유연하고 비공식적인 조직 구조로, 혁신적이고 창의적인 작업 환경에 적합한 구조입니다. 프로젝트별로 팀을 구성하고, 목표 달성을 위해 자유롭게 협력하는 구조로, 스타트업 기업이나 연구소에서 주로 나타납니다.
- 구성요소:
- 운영층 (Operating Core): 다양한 전문가들이 프로젝트별로 팀을 구성하고 자율적으로 작업합니다.
- 중간관리층 (Middle Line): 운영층의 자율적인 작업을 관리하고 조정하는 역할을 합니다.
- 전문직 관리층 (Technostructure): 프로젝트별로 필요한 기술적 지원과 조언을 제공합니다.
- 장점: 유연성, 창의성, 혁신적인 아이디어가 잘 나옵니다.
- 단점: 자원의 낭비와 중복이 발생할 수 있으며, 관리가 어려울 수 있습니다.
5. 단일 과업형 조직 (Simple Structure)
- 특징: 단일 과업형 조직은 소규모의 조직으로, 관리 구조가 간단하고, 의사결정이 빠르고 유연한 구조입니다. 창업 초기의 스타트업이나 가족 경영 기업에서 많이 나타납니다. 상위 경영자가 대부분의 의사결정을 내리며, 매우 단순한 조직 구조를 가집니다.
- 구성요소:
- 최고경영층 (Strategic Apex): 최고경영자가 조직의 모든 전략적 결정을 내립니다.
- 운영층 (Operating Core): 주로 상위 경영자의 지시를 받아 일상적인 업무를 처리하는 직원들입니다.
- 장점: 의사결정이 빠르고, 유연하며, 작은 규모의 조직에 적합합니다.
- 단점: 상위 경영자가 모든 결정을 내리기 때문에 리더십에 대한 의존도가 높고, 성장과 규모 확장에 어려움을 겪을 수 있습니다.
6. 임시 조직 (Missionary Organization)
- 특징: 임시 조직은 강력한 공통의 목표나 사명감에 의해 결속된 조직으로, 종교적, 사회적, 정치적 목적을 가진 조직에서 나타날 수 있습니다. 이 조직은 종종 자율적이고, 공통된 가치를 기반으로 운영됩니다.
- 구성요소:
- 운영층 (Operating Core): 공통된 사명감과 목표를 기반으로 활동하는 직원들입니다.
- 중간관리층 (Middle Line): 운영층을 지원하며 조직의 목표를 실현하기 위한 역할을 합니다.
- 장점: 강한 목표 의식과 결속력으로 높은 동기 부여와 생산성을 얻을 수 있습니다.
- 단점: 외부 환경 변화에 대한 적응이 어려울 수 있으며, 목표가 지나치게 제한적일 수 있습니다.
결론
헨리 민츠버그의 조직 유형 이론은 조직의 구조를 5가지 기본적인 유형과 한 가지 임시적 조직 유형으로 나누어, 각 조직이 어떻게 운영되고 관리되는지에 대한 구체적인 모델을 제시합니다. 각 조직 유형은 특정한 환경과 상황에 적합하며, 조직의 목표나 운영 방식에 따라 적절한 구조를 선택하는 것이 중요합니다. 민츠버그의 이론은 조직이 효율성과 창의성 사이에서 어떻게 균형을 맞추어야 하는지에 대한 중요한 통찰을 제공합니다.
Henry Mintzberg is a notable scholar in the field of organizational theory, known for his research on classifying organizations based on their structure and functions. Mintzberg identifies six types of organizational structures, each suited to different sizes, environments, goals, and management styles. His theory provides insights into how organizations are structured and how each structure operates.
Mintzberg categorized organizations into six primary structures based on organizational components and environment. Each type has unique characteristics, strengths, and weaknesses, and plays a crucial role in understanding the organization's objectives and operations.
Mintzberg's Organizational Types
- Machine Bureaucracy
- Characteristics: Operates with strict rules and standardized procedures, featuring clear role division and centralized decision-making. Commonly found in large corporations and government agencies.
- Components:
- Operating Core: Employees performing routine tasks.
- Middle Line: Managers linking higher management with the operating core.
- Support Staff: Departments supporting the management and frontline employees.
- Technostructure: Experts standardizing processes and procedures.
- Strategic Apex: Top executives making strategic decisions.
- Strengths: Efficient, predictable operations; suitable for large-scale organizations.
- Weaknesses: Lacks creativity and flexibility; struggles with adapting to environmental changes.
- Professional Bureaucracy
- Characteristics: Requires high levels of expertise, with professionals autonomously performing their tasks. Common in hospitals, universities, and accounting firms.
- Components:
- Operating Core: Professionals performing their tasks independently.
- Middle Line: Managers coordinating and supervising the professionals.
- Strategic Apex: Top management supporting professionals in achieving strategic goals.
- Strengths: High-quality services due to specialization; high autonomy.
- Weaknesses: Strong independence among professionals can hinder cooperation; difficult to control.
- Divisionalized Form
- Characteristics: Divides the organization into independent divisions, each with its own management structure. Commonly used by large corporations managing diverse products or regions.
- Components:
- Divisions: Independent segments managing their own operations and resources.
- Technostructure: Standardizing processes across divisions.
- Strategic Apex: Top management setting overall strategy and resource allocation.
- Strengths: Adaptable to market changes; each division operates independently.
- Weaknesses: Resource duplication and lack of coordination; reduced overall coherence.
- Adhocracy
- Characteristics: Highly flexible and informal, suitable for innovative and creative environments. Teams are formed for specific projects, allowing free collaboration. Common in startups and research labs.
- Components:
- Operating Core: Experts forming teams for projects, working autonomously.
- Middle Line: Managers facilitating and coordinating team activities.
- Technostructure: Providing technical support and advice for projects.
- Strengths: High flexibility, creativity, and innovative ideas.
- Weaknesses: Potential for resource waste and redundancy; challenging to manage.
- Simple Structure
- Characteristics: Small-scale organizations with a simple management structure, quick and flexible decision-making. Common in startups and family-run businesses. Top management makes most decisions.
- Components:
- Strategic Apex: Top executive making all strategic decisions.
- Operating Core: Employees executing daily tasks under direct supervision.
- Strengths: Quick, flexible decision-making; suitable for small organizations.
- Weaknesses: High reliance on top leadership; challenges in growth and scaling.
- Missionary Organization
- Characteristics: Bonded by a strong common goal or mission, often found in religious, social, or political organizations. Operates autonomously based on shared values.
- Components:
- Operating Core: Employees motivated by common mission and goals.
- Middle Line: Managers supporting the operating core to achieve objectives.
- Strengths: High motivation and productivity due to strong mission alignment.
- Weaknesses: Difficulty adapting to external changes; overly narrow focus.
Conclusion
Henry Mintzberg's organizational structure theory categorizes organizations into six types, each providing a specific model for how organizations operate and manage. Each type suits particular environments and situations, and choosing the appropriate structure based on organizational goals and operations is crucial. Mintzberg's theory offers valuable insights into balancing efficiency and creativity within organizations.