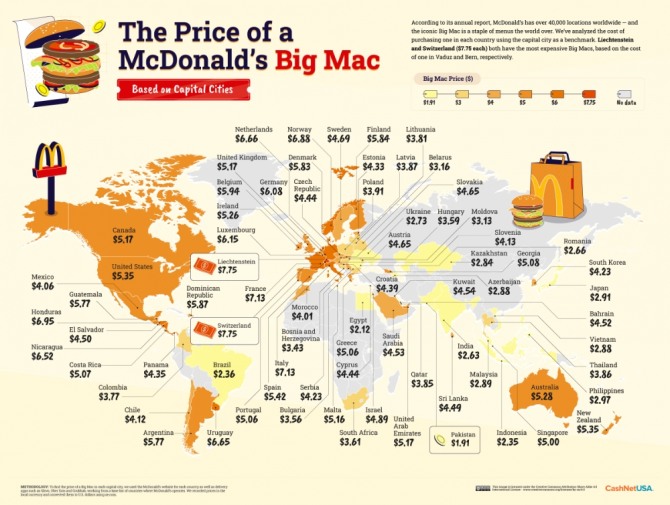
1. 빅맥지수란 무엇인가?
빅맥지수(Big Mac Index)는 특정 국가의 통화 가치가 실제 구매력을 반영하는지를 간단히 평가하기 위해 맥도날드의 빅맥(Big Mac) 햄버거 가격을 비교하는 경제 지표입니다.
1986년 영국의 경제 주간지 The Economist에서 처음 개발했으며, 이후 경제학과 국제 경제 연구에서 널리 사용되고 있습니다.
빅맥지수는 구매력 평가(Purchasing Power Parity, PPP) 개념에 기반을 두고 있습니다. PPP 이론에 따르면, 동일한 상품은 전 세계 어디에서나 같은 가격이어야 한다는 가정을 바탕으로 합니다. 빅맥은 전 세계 대부분의 국가에서 동일한 품질과 구성으로 판매되기 때문에, 이 햄버거의 가격을 기준으로 환율의 적정성을 비교할 수 있습니다.
2. 빅맥지수의 계산 방식
빅맥지수는 각 국가에서 판매되는 빅맥의 현지 통화 가격을 미국 달러로 환산하여 비교합니다.
빅맥지수 환율=해외 빅맥 가격(현지통화)미국 빅맥 가격(USD)\text{빅맥지수 환율} = \frac{\text{해외 빅맥 가격(현지통화)}}{\text{미국 빅맥 가격(USD)}}빅맥지수 환율=미국 빅맥 가격(USD)해외 빅맥 가격(현지통화)
- 실제 환율과 비교하여 과대평가 또는 과소평가 여부를 판단합니다.
- 과대평가: 빅맥지수 환율이 실제 환율보다 낮으면, 해당 통화가 달러 대비 과대평가된 것으로 간주.
- 과소평가: 빅맥지수 환율이 실제 환율보다 높으면, 해당 통화가 달러 대비 과소평가된 것으로 간주.
3. 빅맥지수의 활용
- 환율의 적정성 평가:
- 빅맥지수를 통해 특정 통화가 과대평가 또는 과소평가되었는지 간단히 확인할 수 있습니다.
- 예: 2024년 기준, 중국 위안화가 빅맥지수 상 과소평가되어 있다면, 중국 내 빅맥이 미국보다 상대적으로 저렴함을 의미합니다.
- 구매력 평가 지표로서의 역할:
- 빅맥지수는 세계 각국의 물가 수준을 단순 비교하는 도구로도 사용됩니다.
- 국가 간 생활비 차이를 파악하는 데 유용합니다.
- 경제 트렌드 분석:
- 장기간의 빅맥지수 변화를 통해 특정 국가의 물가 상승, 환율 변동, 경제 상황을 추적할 수 있습니다.
4. 빅맥지수의 한계와 비판
- 비교 대상 상품의 제한성:
빅맥은 전 세계적으로 표준화된 제품이지만, 각국의 경제적, 문화적 특성을 모두 반영하지는 못합니다.- 예: 노동 비용, 재료 비용, 세금, 유통비 등.
- 소비 패턴의 차이:
빅맥은 일부 국가에서 일상적으로 소비되지 않거나 사치품으로 여겨질 수 있습니다.- 예: 저소득 국가에서는 빅맥이 일반 소비자의 구매력이 아닌 프리미엄 제품으로 간주될 수 있음.
- 구매력 평가의 한계:
빅맥지수는 단순한 비교를 위한 도구이며, 실제 경제 상황을 정밀하게 분석하는 데는 한계가 있습니다.- 예: 에너지, 주거, 교통 등 다양한 요소를 포함하지 않음.
5. 빅맥지수의 실제 사례
- 2023년 기준 빅맥지수:
- 미국: $5.36
- 스위스: $6.95 (달러 대비 과대평가)
- 인도: $2.23 (달러 대비 과소평가)
스위스의 경우 빅맥 가격이 미국보다 높아 스위스 프랑이 달러 대비 과대평가된 것으로 나타납니다. 반면, 인도의 빅맥 가격이 매우 낮아 인도 루피는 달러 대비 과소평가된 것으로 간주됩니다.
6. 빅맥지수의 현대적 응용
최근에는 전통적인 빅맥지수 외에도, 경제 상황을 보다 정확히 반영하기 위해 조정된 지수도 사용됩니다.
- 조정 빅맥지수: 노동 비용과 생활비를 반영하여 기존 지수의 한계를 보완한 방식.
- 스타벅스 라떼 지수: 빅맥 외에도 다른 글로벌 상품을 사용한 유사 지표.
1. What is the Big Mac Index?
The Big Mac Index is an economic indicator used to evaluate whether the exchange rate of a currency accurately reflects its purchasing power. It compares the price of a Big Mac hamburger across different countries. Developed by the British weekly magazine The Economist in 1986, it is widely used in economics and international economic studies.
The Big Mac Index is based on the concept of Purchasing Power Parity (PPP). According to the PPP theory, identical goods should have the same price worldwide. Since the Big Mac is sold in a standardized form in most countries, its price serves as a basis for comparing exchange rate fairness.
2. How the Big Mac Index is Calculated
The Big Mac Index is calculated by converting the local price of a Big Mac in each country into US dollars and comparing it.
Comparing this rate with the actual exchange rate helps determine if a currency is overvalued or undervalued:
- Overvalued: If the Big Mac Index exchange rate is lower than the actual exchange rate, the currency is considered overvalued against the dollar.
- Undervalued: If the Big Mac Index exchange rate is higher than the actual exchange rate, the currency is considered undervalued against the dollar.
3. Applications of the Big Mac Index
- Assessing Exchange Rate Fairness: The Big Mac Index provides a simple way to check if a currency is overvalued or undervalued.
- Example: As of 2024, if the Chinese yuan is undervalued according to the Big Mac Index, it means a Big Mac is cheaper in China than in the US.
- Indicator of Purchasing Power: The Big Mac Index is also used to compare the price levels of various countries.
- It is useful for understanding differences in the cost of living between countries.
- Analyzing Economic Trends: Long-term changes in the Big Mac Index can help track inflation, exchange rate fluctuations, and economic conditions in specific countries.
4. Limitations and Criticisms of the Big Mac Index
- Limitations of the Compared Product: Although the Big Mac is a standardized product globally, it does not fully reflect the economic and cultural characteristics of each country.
- Examples: Labor costs, ingredient costs, taxes, and distribution costs.
- Differences in Consumption Patterns: The Big Mac might not be a common daily purchase or could be considered a luxury item in some countries.
- Example: In low-income countries, the Big Mac may be seen as a premium product rather than something an average consumer can afford regularly.
- Limitations of Purchasing Power Evaluation: The Big Mac Index is a tool for simple comparisons and is limited in precisely analyzing actual economic situations.
- Example: It does not account for various factors such as energy, housing, and transportation costs.
5. Real-World Examples of the Big Mac Index
- 2023 Big Mac Index:
- United States: $5.36
- Switzerland: $6.95 (overvalued against the dollar)
- India: $2.23 (undervalued against the dollar)
In Switzerland, the higher price of the Big Mac indicates that the Swiss franc is overvalued against the dollar. Conversely, the much lower price in India suggests the Indian rupee is undervalued against the dollar.
6. Modern Applications of the Big Mac Index
Recently, adjusted indices have been used to more accurately reflect economic conditions beyond the traditional Big Mac Index.
- Adjusted Big Mac Index: This version accounts for labor costs and living expenses to address the original index's limitations.
- Starbucks Latte Index: Similar to the Big Mac Index but uses other global products like a Starbucks latte for comparison.
The Big Mac Index remains a popular and straightforward tool for comparing purchasing power across countries, despite its limitations.