로렌츠 곡선(Lorenz Curve)은 소득 분포나 자산 분포의 불평등을 시각적으로 나타내는 그래프입니다. 주로 경제학에서 사용되며, 소득이나 자산의 분포가 얼마나 평등하게 또는 불평등하게 이루어져 있는지를 분석하는 데 유용합니다. 이 곡선은 1905년에 경제학자 마كس 로렌츠(Maks Lorenz)에 의해 제안되었습니다.
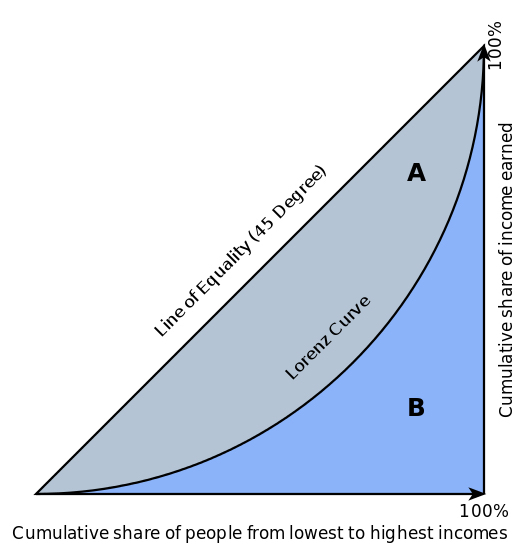
로렌츠 곡선의 구성 요소:
- X축 (수평축): 인구의 누적 백분율을 나타냅니다. 예를 들어, 0%는 가장 낮은 소득을 가진 사람을 의미하고, 100%는 전체 인구를 의미합니다.
- Y축 (수직축): 해당 인구가 가진 소득이나 자산의 누적 백분율을 나타냅니다. 즉, X축에 해당하는 인구가 가진 전체 소득의 비율입니다.
- 대각선 (45도 직선): 완전 평등을 나타내는 기준선입니다. 이 직선에서는 인구의 20%가 전체 소득의 20%를 가지는 등, 모든 사람들이 동일한 비율로 소득을 가진다고 가정하는 이상적인 평등 상태를 나타냅니다.
로렌츠 곡선의 특징:
- 평등 분포: 로렌츠 곡선이 대각선(45도 직선)과 일치하면, 모든 사람의 소득이 동일하게 분포되어 있음을 의미합니다. 즉, 완전한 소득 평등 상태입니다.
- 불평등 분포: 로렌츠 곡선이 대각선에서 멀어질수록, 소득이나 자산의 분포가 불평등함을 나타냅니다. 즉, 일부 사람들이 많은 소득을 차지하고 다른 사람들은 적은 소득을 가진 경우입니다.
로렌츠 곡선의 활용:
로렌츠 곡선은 소득 분포의 불평등 정도를 측정하는 중요한 도구입니다. 이 곡선의 면적을 통해 불평등의 정도를 수치적으로 나타낼 수 있습니다.
지니 계수 (Gini Coefficient):
- 로렌츠 곡선의 면적을 이용해 **지니 계수(Gini Index)**를 계산할 수 있습니다. 지니 계수는 소득 불평등의 정도를 나타내는 지표로, 0과 1 사이의 값을 가집니다.
- 지니 계수 0: 완전 평등 상태 (모든 사람이 같은 소득)
- 지니 계수 1: 완전 불평등 상태 (하나의 사람이 모든 소득을 차지)
지니 계수는 로렌츠 곡선 아래 면적을 활용하여 계산되며, 이 값이 클수록 소득이나 자산의 분포가 불평등하다는 것을 의미합니다.
로렌츠 곡선 예시:
- 완전 평등: 모든 사람에게 동일한 소득이 분배될 경우, 로렌츠 곡선은 대각선(45도 직선)과 일치합니다.
- 완전 불평등: 한 사람만 모든 소득을 차지하는 경우, 로렌츠 곡선은 X축과 Y축을 따라가게 됩니다. 이는 완전히 비효율적이고 불평등한 소득 분포를 나타냅니다.
요약:
로렌츠 곡선은 소득이나 자산의 분포가 얼마나 평등한지, 또는 불평등한지를 시각적으로 보여주는 도구입니다. 이 곡선을 통해 불평등을 분석할 수 있으며, 지니 계수 같은 수치를 통해 이를 수치적으로 평가할 수 있습니다.
Lorenz Curve is a graphical representation used to visually depict the inequality of income or wealth distribution. It is mainly used in economics to analyze how equally or unequally income or wealth is distributed. This curve was proposed by economist Max Lorenz in 1905.
Components of the Lorenz Curve:
- X-axis (Horizontal Axis): Represents the cumulative percentage of the population. For example, 0% represents the person with the lowest income, and 100% represents the entire population.
- Y-axis (Vertical Axis): Represents the cumulative percentage of income or wealth owned by the corresponding population percentage on the X-axis.
- Diagonal Line (45-degree line): Represents perfect equality. This line indicates an ideal state where, for example, 20% of the population owns 20% of the total income, and so on.
Features of the Lorenz Curve:
- Equal Distribution: When the Lorenz Curve coincides with the diagonal line, it indicates that income is equally distributed among the population, representing perfect income equality.
- Unequal Distribution: The further the Lorenz Curve is from the diagonal line, the more unequal the distribution of income or wealth. This means some people have a lot of income while others have very little.
Uses of the Lorenz Curve:
The Lorenz Curve is an important tool for measuring the degree of income inequality. The area under the curve can be used to quantify the level of inequality.
Gini Coefficient:
The Gini Coefficient is calculated using the area under the Lorenz Curve. It is a measure of income inequality, ranging from 0 to 1.
- Gini Coefficient 0: Perfect equality (everyone has the same income)
- Gini Coefficient 1: Perfect inequality (one person has all the income) The larger the Gini Coefficient, the more unequal the distribution of income or wealth.
Examples of the Lorenz Curve:
- Perfect Equality: If income is distributed equally among all individuals, the Lorenz Curve would coincide with the diagonal line.
- Perfect Inequality: If one person owns all the income, the Lorenz Curve would follow the X and Y axes, indicating a completely unequal and inefficient distribution of income.
Summary:
The Lorenz Curve is a visual tool that shows how equal or unequal the distribution of income or wealth is. It helps in analyzing inequality, and the Gini Coefficient quantifies this inequality numerically.