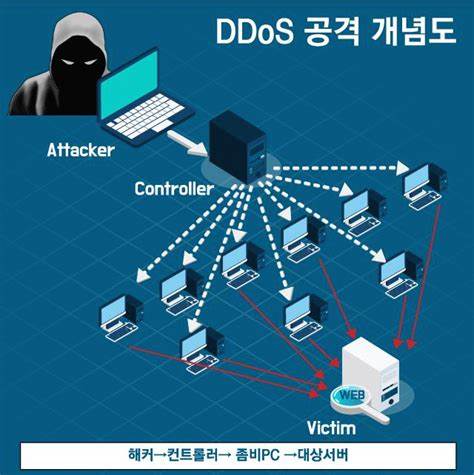
DDoS(Distributed Denial of Service, 분산 서비스 거부) 공격은 여러 대의 컴퓨터나 장치를 이용해 특정 웹사이트나 서버에 과도한 트래픽을 보내서 해당 서비스나 네트워크가 정상적으로 작동하지 못하게 만드는 사이버 공격입니다.
DDoS 공격의 주된 목적은 서비스의 중단을 일으켜 피해를 주는 것입니다.
DDoS 공격의 작동 원리
- 보내는 측: DDoS 공격은 하나의 장치가 아닌 여러 대의 장치에서 동시에 공격이 이루어집니다. 공격에 사용되는 장치들은 종종 악성코드에 감염된 컴퓨터나 IoT 기기들로, 이를 **봇넷(botnet)**이라고 부릅니다. 봇넷은 공격자가 원격으로 제어할 수 있는 장치들의 네트워크입니다.
- 공격의 목표: DDoS 공격은 일반적으로 특정 서버나 네트워크 장비를 목표로 하며, 공격자가 제어하는 봇넷에서 동시에 트래픽을 보내 서버의 자원을 과도하게 소모시킵니다. 이로 인해 서버가 응답을 하지 않거나, 과중한 트래픽으로 인해 정상적인 사용자가 웹사이트에 접속할 수 없게 됩니다.
- 공격의 방식:
- Flooding Attack(플러딩 공격): 공격자가 서버에 과도한 트래픽을 보내 서비스가 마비되도록 하는 방식입니다. 가장 일반적인 방법은 서버에 대량의 데이터를 요청하거나, 서버에 너무 많은 연결을 시도하는 것입니다.
- Amplification Attack(증폭 공격): 공격자가 상대 서버에 작은 요청을 보내고, 그 서버가 더 큰 응답을 반환하도록 유도하여 상대방 서버에 과도한 부담을 주는 방식입니다. 예를 들어, DNS 서버를 이용한 공격은 소량의 요청을 보내고, 대량의 응답을 목표 서버로 되돌려 보내는 방식입니다.
DDoS 공격의 종류
- HTTP Flood: 웹 애플리케이션의 취약점을 이용하여 과도한 HTTP 요청을 보내 서버를 과부하시키는 공격입니다. 이는 웹사이트의 서버 리소스를 소모하게 해 웹페이지 로딩을 지연시키거나 서버를 다운시킬 수 있습니다.
- SYN Flood: TCP 연결을 설정하는 과정에서 SYN 패킷을 지속적으로 보내 서버가 자원을 소모하도록 만드는 공격입니다. 연결 요청을 보내지만 응답을 하지 않아 서버는 계속 대기 상태에 빠지게 됩니다.
- UDP Flood: 사용되지 않는 UDP 포트를 목표로 하여 대량의 UDP 패킷을 보내 서버가 해당 패킷을 처리하기 위해 리소스를 소모하도록 유도하는 공격입니다.
- NTP Amplification: 네트워크 시간 프로토콜(NTP) 서버를 악용해 작은 요청에 대해 큰 응답을 반환하게 하여 공격 대상에 큰 트래픽을 발생시킵니다.
DDoS 공격의 대응 방법
- 트래픽 필터링: 공격이 발생하면 방화벽이나 로드 밸런서를 사용해 공격 트래픽을 필터링하거나 차단할 수 있습니다.
- 클라우드 기반 방어: 많은 기업들이 클라우드 기반 DDoS 방어 솔루션을 사용해 대규모 트래픽을 처리하거나 필터링하는 방안을 채택하고 있습니다. 이들은 대규모 분산 트래픽을 처리할 수 있는 인프라를 제공해 DDoS 공격을 완화시킵니다.
- Rate Limiting(속도 제한): 특정 IP 주소에서 과도한 트래픽이 발생하지 않도록 요청의 수를 제한할 수 있습니다.
- 패턴 분석: 공격 트래픽의 패턴을 분석하여 정상 트래픽과 공격 트래픽을 구별하고, 공격을 더 빠르게 차단할 수 있습니다.
DDoS 공격의 영향
DDoS 공격은 비즈니스 운영에 심각한 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 온라인 쇼핑몰, 금융 기관, 게임 서버 등의 서비스가 마비되면 사용자는 서비스를 이용할 수 없고, 기업은 수익 손실, 고객 신뢰도 하락, 평판 문제 등의 문제에 직면할 수 있습니다.
결론
DDoS 공격은 점점 더 강력하고, 교묘하게 진화하고 있습니다. 공격자는 봇넷을 사용해 동시에 여러 대의 장치에서 공격을 시도하며, 기업들은 이를 방어하기 위해 다양한 보안 기술과 인프라를 강화하고 있습니다. DDoS 공격의 피해를 줄이기 위해서는 보안 솔루션을 강화하고, 공격에 대한 사전 대비를 하는 것이 중요합니다.
DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks involve using multiple computers or devices to send excessive traffic to a specific website or server, causing the service or network to malfunction. The main purpose of a DDoS attack is to disrupt service and cause damage.
How DDoS Attacks Work
- Attack Source: DDoS attacks are carried out from multiple devices simultaneously, not just one. The devices used in the attack are often infected with malware, forming a network called a botnet. A botnet is a network of devices that an attacker can remotely control.
- Attack Target: DDoS attacks typically target specific servers or network equipment, with botnets simultaneously sending traffic to exhaust the server's resources. This can cause the server to become unresponsive, preventing normal users from accessing the website.
- Attack Methods:
- Flooding Attack: Attackers send excessive traffic to the server, causing the service to become paralyzed. This usually involves requesting a large amount of data from the server or making too many connection attempts.
- Amplification Attack: Attackers send small requests to a server, which then returns larger responses, placing excessive load on the target server. For example, in a DNS amplification attack, small requests are sent to a DNS server, which returns large responses to the target server.
Types of DDoS Attacks
- HTTP Flood: This attack exploits vulnerabilities in web applications by sending excessive HTTP requests to overload the server, causing web pages to load slowly or the server to go down.
- SYN Flood: This attack involves continuously sending SYN packets during the TCP connection process, causing the server to consume resources. The attack sends connection requests without responding to them, leaving the server in a waiting state.
- UDP Flood: This attack targets unused UDP ports by sending a large number of UDP packets, forcing the server to consume resources to process these packets.
- NTP Amplification: This attack exploits Network Time Protocol (NTP) servers to return large responses to small requests, generating significant traffic toward the target.
Mitigation Methods for DDoS Attacks
- Traffic Filtering: When an attack occurs, firewalls or load balancers can be used to filter or block attack traffic.
- Cloud-based Defense: Many companies use cloud-based DDoS protection solutions to handle or filter large volumes of traffic. These solutions provide infrastructure capable of processing large distributed traffic, mitigating the DDoS attack.
- Rate Limiting: This involves limiting the number of requests from specific IP addresses to prevent excessive traffic.
- Pattern Analysis: By analyzing the patterns of attack traffic, normal traffic can be distinguished from attack traffic, allowing quicker mitigation of the attack.
Impact of DDoS Attacks
DDoS attacks can have serious impacts on business operations. For example, if an online shopping mall, financial institution, or gaming server is paralyzed, users cannot access the service, and the company faces revenue loss, customer trust decline, and reputation issues.
Conclusion
DDoS attacks are becoming increasingly powerful and sophisticated. Attackers use botnets to simultaneously launch attacks from multiple devices, and companies are strengthening their security technologies and infrastructure to defend against them. Enhancing security solutions and preparing for attacks in advance is crucial to minimizing the damage caused by DDoS attacks.