사물인터넷(Internet of Things, IoT)은 물리적인 사물들이 인터넷을 통해 서로 연결되어 데이터를 주고받고, 이를 통해 스마트한 서비스를 제공하는 기술입니다. 간단히 말하면, 사물인터넷은 일상적인 기기나 물건들이 인터넷과 연결되어 정보를 주고받으며, 이를 통해 사람들의 생활을 더 편리하고 효율적으로 만드는 시스템입니다.
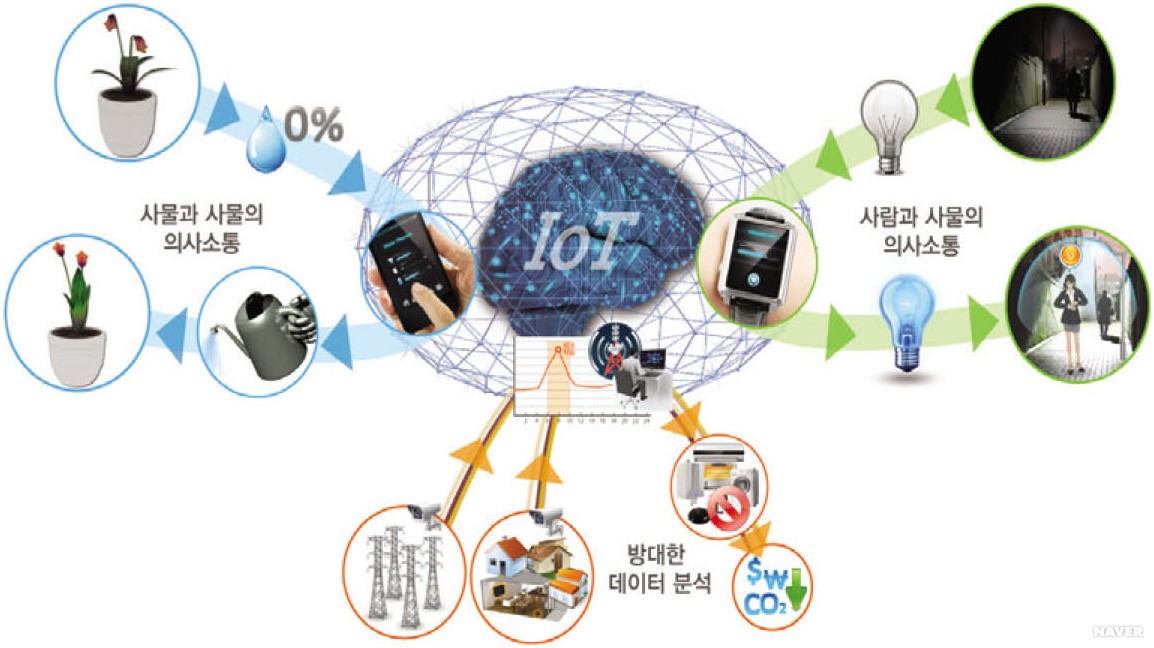
1. 사물인터넷(IoT)의 정의
사물인터넷은 **‘사물’**이란 물리적 객체나 기기가 인터넷에 연결되어 데이터를 수집하고 이를 네트워크를 통해 전송하거나 다른 기기들과 상호작용을 하는 기술입니다. IoT는 센서, 연결성, 데이터 처리 및 자동화를 핵심으로 하여, 다양한 디바이스들이 상호작용하며 유기적으로 작동합니다.
2. 사물인터넷의 주요 구성 요소
사물인터넷은 몇 가지 중요한 기술 요소로 구성됩니다:
(1) 디바이스(Devices)
사물인터넷의 핵심은 인터넷에 연결된 장치들입니다. 이 장치들은 다양한 센서와 액추에이터를 통해 데이터를 수집하고, 외부 시스템과 연결됩니다. 예를 들어, 스마트폰, 스마트 스피커, 스마트 냉장고, 웨어러블 기기 등이 사물인터넷 장치의 예시입니다.
(2) 센서(Sensors)
센서는 사물인터넷에서 데이터를 수집하는 중요한 역할을 합니다. 온도, 습도, 압력, 위치, 속도 등을 측정하는 센서들은 실시간 데이터를 받아들여 시스템의 중앙 처리 장치로 전달합니다. 예를 들어, 스마트홈에서 온도를 측정하는 온도 센서, 스마트 농업에서 토양의 수분을 측정하는 센서 등이 있습니다.
(3) 네트워크(Networks)
IoT 장치들은 데이터를 실시간으로 전송하기 위해 인터넷 연결을 필요로 합니다. Wi-Fi, 블루투스, 5G, LoRaWAN 등 다양한 네트워크 기술들이 IoT 장치와 연결되어 데이터를 주고받습니다. 안정적인 네트워크는 IoT 시스템의 핵심입니다.
(4) 클라우드(Cloud)
사물인터넷에서 수집된 방대한 양의 데이터를 처리하고 저장하기 위해 클라우드 서비스가 중요한 역할을 합니다. 클라우드는 데이터를 분석하고 저장하는 곳으로, 실시간 데이터 처리를 가능하게 하며, 여러 IoT 장치 간에 통합된 서비스를 제공합니다.
(5) 데이터 처리 및 분석(Data Processing and Analytics)
IoT 시스템은 센서를 통해 데이터를 수집하고 이를 분석하여 의미 있는 정보를 도출합니다. 빅데이터와 인공지능(AI) 기술을 통해 수집된 데이터를 분석하고 예측하는 능력을 갖추면, 더욱 스마트한 결정을 내릴 수 있습니다.
3. 사물인터넷의 주요 기술
사물인터넷의 발전을 위해 다양한 기술들이 결합되어 있습니다:
(1) 센서 기술
센서는 IoT의 가장 기본적인 요소로, 실시간 데이터를 수집하는 데 사용됩니다. 온도 센서, 압력 센서, GPS, 카메라 등 다양한 형태의 센서들이 있습니다. IoT 시스템에서 데이터를 수집하고 이를 실시간으로 전송하는 역할을 합니다.
(2) 통신 기술
사물인터넷 기기들 간의 원활한 연결을 위해 통신 기술이 필수적입니다. Wi-Fi, 블루투스, ZigBee, 5G, LoRaWAN 등이 주요 통신 기술로, 각 기술은 사용되는 환경과 데이터 전송 범위에 따라 선택됩니다.
(3) 클라우드 컴퓨팅
사물인터넷 기기들이 수집한 방대한 양의 데이터를 저장하고 분석하는 데 클라우드 컴퓨팅이 사용됩니다. 클라우드는 대용량 데이터 저장과 실시간 데이터 처리를 가능하게 하며, IoT 기기 간의 효율적인 통합을 돕습니다.
(4) 인공지능(AI) 및 머신러닝
IoT에서 수집된 데이터는 AI와 머신러닝을 통해 분석되며, 이를 바탕으로 자동화된 의사결정이 이루어집니다. 예를 들어, 스마트홈에서는 사용자의 생활 패턴을 분석하여 자동으로 온도나 조명을 조정하는 AI 기반 시스템이 작동합니다.
(5) 보안 기술
사물인터넷은 다양한 장치들이 연결되는 만큼 보안도 중요한 요소입니다. 암호화와 인증 시스템을 통해 IoT 시스템의 안전성을 확보하고, 해킹이나 사이버 공격으로부터 보호해야 합니다.
4. 사물인터넷의 활용 분야
사물인터넷은 다양한 산업과 분야에서 폭넓게 활용되고 있습니다.
(1) 스마트홈(Smart Home)
스마트홈은 IoT 기술을 이용하여 가정 내의 기기들을 자동으로 제어하고 모니터링하는 시스템입니다. 스마트 조명, 스마트 온도조절기, 스마트 보안 시스템 등 다양한 IoT 기기들이 실시간으로 연결되어, 사용자가 스마트폰을 통해 집안의 모든 것을 제어할 수 있습니다.
(2) 헬스케어(Healthcare)
IoT는 의료 분야에서도 큰 혁신을 일으키고 있습니다. 웨어러블 기기(예: 스마트워치)는 사용자의 건강 상태를 실시간으로 모니터링하고, 이를 통해 심박수, 혈압, 운동량 등을 측정할 수 있습니다. 또한, 원격 의료 서비스가 활성화되면서, 의사와 환자가 IoT 기기를 통해 실시간으로 연결되는 시스템이 구축되고 있습니다.
(3) 스마트 시티(Smart City)
IoT는 도시를 더욱 효율적으로 만들기 위한 스마트 시티 구축에 중요한 역할을 합니다. 교통 시스템, 에너지 관리, 환경 모니터링 등이 IoT 기술을 통해 관리되며, 시민들의 삶의 질을 높이는 데 기여하고 있습니다. 예를 들어, 스마트 주차 시스템이나 스마트 쓰레기통이 운영되고 있습니다.
(4) 산업 자동화(Industry 4.0)
산업 분야에서 IoT는 스마트 팩토리를 구축하는 데 필수적입니다. 생산 라인에 IoT 기기를 설치하여 자동화된 공정 관리, 설비 모니터링, 예측 유지보수 등을 수행하며, 생산성을 향상시키고 비용을 절감할 수 있습니다.
(5) 농업(Agriculture)
스마트 농업에서는 IoT 기술을 활용하여 농작물의 생장 상태, 토양의 수분 수준, 기후 데이터 등을 실시간으로 모니터링하고 분석합니다. 이를 통해 농업 생산성을 극대화하고, 자원의 낭비를 줄일 수 있습니다.
5. 사물인터넷의 도전 과제
(1) 보안 문제
IoT 장치들이 늘어날수록 보안 문제는 더욱 중요해집니다. 해커들이 IoT 기기를 통해 시스템을 공격하거나 개인정보를 탈취할 수 있기 때문에, 강력한 보안 기술과 암호화가 필요합니다.
(2) 데이터 처리 및 저장
IoT는 막대한 양의 데이터를 생성하므로 이를 처리하고 저장하는 데 필요한 데이터 처리 능력과 클라우드 인프라가 필수적입니다. 이러한 방대한 데이터를 실시간으로 분석하고 효율적으로 관리하는 기술이 필요합니다.
(3) 표준화 부족
IoT 장치들이 서로 통신하기 위해서는 표준화가 필요합니다. 다양한 제조사에서 나오는 기기들이 서로 호환될 수 있도록 하는 표준화 작업이 중요한 과제입니다.
(4) 배터리 수명
사물인터넷 기기들이 오래 작동하기 위해서는 배터리 수명이 중요한 문제입니다. 특히, 배터리 교체가 어려운 IoT 기기에서는 긴 배터리 수명과 효율적인 에너지 관리가 필요합니다.
6. 사물인터넷의 미래 전망
사물인터넷은 앞으로 더욱 발전할 것이며, 우리의 일상과 산업 전반에 걸쳐 핵심적인 역할을 하게 될 것입니다. 5G와 AI의 발전으로 더 빠르고 효율적인 데이터 처리가 가능해지고, 더욱 스마트하고 연결된 세상이 될 것입니다. 또한, 스마트 시티, 스마트 팩토리, 스마트 홈 등 다양한 분야에서 IoT의 영향력이 계속 확대될 것입니다.
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the technology where physical objects are connected to the internet to exchange data and provide smart services. Simply put, IoT involves everyday devices or objects connecting to the internet to send and receive information, thus making people’s lives more convenient and efficient.
1. Definition of IoT
IoT involves 'things'—physical objects or devices connected to the internet to collect and transmit data through a network, interacting with other devices. IoT encompasses sensors, connectivity, data processing, and automation, allowing various devices to interact and work organically.
2. Key Components of IoT
IoT consists of several essential technological components:
- Devices The core of IoT is the devices connected to the internet. These devices collect data through various sensors and actuators and connect to external systems. Examples include smartphones, smart speakers, smart refrigerators, and wearable devices.
- Sensors Sensors play a crucial role in IoT by collecting data. Sensors measuring temperature, humidity, pressure, location, and speed receive real-time data and transmit it to the system’s central processing unit. Examples include temperature sensors in smart homes and moisture sensors in smart agriculture.
- Networks IoT devices require internet connectivity to transmit data in real-time. Technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, 5G, and LoRaWAN connect IoT devices to exchange data. A stable network is vital to the IoT system.
- Cloud Cloud services play an essential role in processing and storing the vast amounts of data collected in IoT. The cloud analyzes and stores data, enables real-time data processing, and provides integrated services among various IoT devices.
- Data Processing and Analytics IoT systems collect data through sensors and analyze it to derive meaningful information. Equipped with capabilities to analyze and predict data using Big Data and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies, smarter decisions can be made.
3. Key Technologies of IoT
Various technologies are combined to advance IoT:
- Sensor Technology Sensors are the fundamental elements of IoT, used to collect real-time data. Types of sensors include temperature sensors, pressure sensors, GPS, and cameras. They collect data in IoT systems and transmit it in real-time.
- Communication Technology Communication technology is essential for smooth connections between IoT devices. Major communication technologies include Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, ZigBee, 5G, and LoRaWAN, chosen based on the environment and data transmission range.
- Cloud Computing Cloud computing is used to store and analyze the vast amounts of data collected by IoT devices. The cloud enables large-scale data storage, real-time data processing, and efficient integration among IoT devices.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning The data collected in IoT is analyzed using AI and machine learning, enabling automated decision-making. For example, AI-based systems in smart homes analyze users' lifestyle patterns to automatically adjust temperatures or lighting.
- Security Technology Security is a crucial element in IoT due to the connection of various devices. Encryption and authentication systems secure IoT systems and protect against hacking or cyber-attacks.
4. Applications of IoT
IoT is widely applied across various industries and fields:
- Smart Home Smart homes use IoT technology to automatically control and monitor home devices. Various IoT devices such as smart lighting, smart thermostats, and smart security systems are connected in real-time, allowing users to control everything at home via their smartphones.
- Healthcare IoT brings significant innovation to healthcare. Wearable devices (e.g., smartwatches) monitor users' health conditions in real-time, measuring heart rate, blood pressure, and physical activity. Additionally, with the activation of remote healthcare services, systems are established where doctors and patients connect in real-time via IoT devices.
- Smart City IoT plays a critical role in building smart cities to make urban areas more efficient. Traffic systems, energy management, and environmental monitoring are managed through IoT technology, improving citizens' quality of life. Examples include smart parking systems and smart garbage bins.
- Industrial Automation (Industry 4.0) In the industrial field, IoT is essential for building smart factories. Installing IoT devices in production lines enables automated process management, equipment monitoring, and predictive maintenance, enhancing productivity and reducing costs.
- Agriculture Smart agriculture uses IoT technology to monitor and analyze crop growth conditions, soil moisture levels, and climate data in real-time. This maximizes agricultural productivity and reduces resource wastage.
5. Challenges of IoT
- Security Issues As the number of IoT devices increases, security issues become more critical. Robust security technology and encryption are necessary to protect IoT systems from attacks or personal data breaches by hackers.
- Data Processing and Storage IoT generates massive amounts of data, requiring data processing capabilities and cloud infrastructure for storage and processing. Technologies that can analyze and manage this vast data in real-time are essential.
- Lack of Standardization Standardization is needed for IoT devices to communicate with each other. Standardization efforts are crucial to ensure devices from various manufacturers are compatible.
- Battery Life Battery life is a significant issue for the long operation of IoT devices. Efficient energy management and long battery life are essential, especially for IoT devices where replacing batteries is challenging.
6. Future Outlook of IoT
IoT will continue to develop and play a central role in our daily lives and across industries. With advancements in 5G and AI, faster and more efficient data processing will become possible, leading to a smarter and more connected world. IoT's influence will continue to expand in fields such as smart cities, smart factories, and smart homes.
Chinese Translation
物联网(Internet of Things,IoT)指通过互联网连接物理对象以交换数据并提供智能服务的技术。简而言之,物联网涉及日常设备或物品连接到互联网以发送和接收信息,从而使人们的生活更方便和高效。
1. 物联网的定义
物联网涉及“物”——连接到互联网以收集和传输数据并与其他设备交互的物理对象或设备。物联网涵盖传感器、连接性、数据处理和自动化,允许各种设备互动并有机地工作。
2. 物联网的关键组成部分
物联网由几个重要的技术组件构成:
- 设备(Devices) 物联网的核心是连接到互联网的设备。这些设备通过各种传感器和执行器收集数据并连接到外部系统。示例包括智能手机、智能音箱、智能冰箱和可穿戴设备。
- 传感器(Sensors) 传感器在物联网中发挥着关键作用,通过收集数据。测量温度、湿度、压力、位置和速度的传感器接收实时数据并将其传输到系统的中央处理单元。示例包括智能家居中的温度传感器和智能农业中的湿度传感器。
- 网络(Networks) 物联网设备需要互联网连接以实时传输数据。Wi-Fi、蓝牙、5G和LoRaWAN等技术连接物联网设备以交换数据。稳定的网络对物联网系统至关重要。
- 云(Cloud) 云服务在处理和存储物联网中收集的大量数据方面起重要作用。云分析和存储数据,实现实时数据处理,并在各种物联网设备之间提供集成服务。
- 数据处理和分析(Data Processing and Analytics) 物联网系统通过传感器收集数据并进行分析,以得出有意义的信息。借助大数据和人工智能(AI)技术分析和预测数据,能够做出更智能的决策。
3. 物联网的关键技术
为了推进物联网,结合了各种技术:
- 传感器技术 传感器是物联网的基本要素,用于收集实时数据。传感器类型包括温度传感器、压力传感器、GPS和摄像头。它们在物联网系统中收集数据并实时传输。
- 通信技术 通信技术对物联网设备之间的顺畅连接至关重要。主要通信技术包括Wi-Fi、蓝牙、ZigBee、5G和LoRaWAN,根据环境和数据传输范围选择使用。
- 云计算 云计算用于存储和分析物联网设备收集的大量数据。云实现大规模数据存储、实时数据处理,并帮助物联网设备之间的高效集成。
- 人工智能(AI)和机器学习 物联网收集的数据通过AI和机器学习进行分析,进行自动化决策。例如,智能家居中的AI系统分析用户的生活模式,自动调节温度或照明。
- 安全技术 安全是物联网的重要元素,因为连接了各种设备。加密和认证系统确保物联网系统的安全,防止黑客攻击或网络攻击。
4. 物联网的应用
物联网在各个行业和领域得到广泛应用:
- 智能家居(Smart Home) 智能家居利用物联网技术自动控制和监控家庭设备。各种物联网设备如智能照明、智能恒温器和智能安防系统实时连接,用户可通过智能手机控制家中的一切。
- 医疗保健(Healthcare) 物联网为医疗保健带来重大创新。可穿戴设备(如智能手表